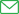
Have you ever wondered exactly how solar panels generate electricity? As you probably already know, Solar panels get their energy from the sun. Below is an outline in four brief steps of how the general process works.
How Solar Panels Work
- Sunlight hits the solar panels and generates an electric DC (Direct energy) current.
- The electric current flows to the inverter, which converts the Direct current into AC (alternating current), which is the most commonly used form of electricity.
- The AC electricity flows from the inverter into the breaker box, which then re-directs this current into any appliance that requires electricity (Washing machines, lights, dishwashers, kettles).
- Any excess electricity flows through a utility meter into the grid (which is the main city’s or town’s electricity supply). Then, if the house needs that electricity back, it can be redrawn from the grid.
The Science Of Photo-Voltaic Cells
Solar PV panels are made up of many small photo-voltaic cells. Photo-voltaic simply means that they can convert sunlight into electricity. These cells are made up of semi-conductive materials, the most common is silicone. This is because it can conduct electricity while still maintaining the electrical imbalance needed to create an electric field.
When the sun’s rays meet the semiconductor, the energy from the light (in photons) is absorbed by the panels. The sun’s energy knocks some electrons loose, which allows them to freely flow within the cells. The cells themselves are designed in such a way that they are both positively, and negatively charged semiconductors, which are sandwiched together in order to create an electric field. The electric field directs the loose electrons into the conductive metal plates that line the outside of the solar cell. Once the metal plates are in contact with the electrons, this current is then directed into wires and flows freely through the wires before hitting the inverter.